On November 17, Professor Jin Lin's team of the College of Animal Medicine published an online report entitled "Interference with LTβR signaling by tick saliva facilitates transmission of Lyme disease spirochetes" in PNAS (2022 impact factor/JCR partition: 13.451/Q1), an international famous comprehensive academic journal.
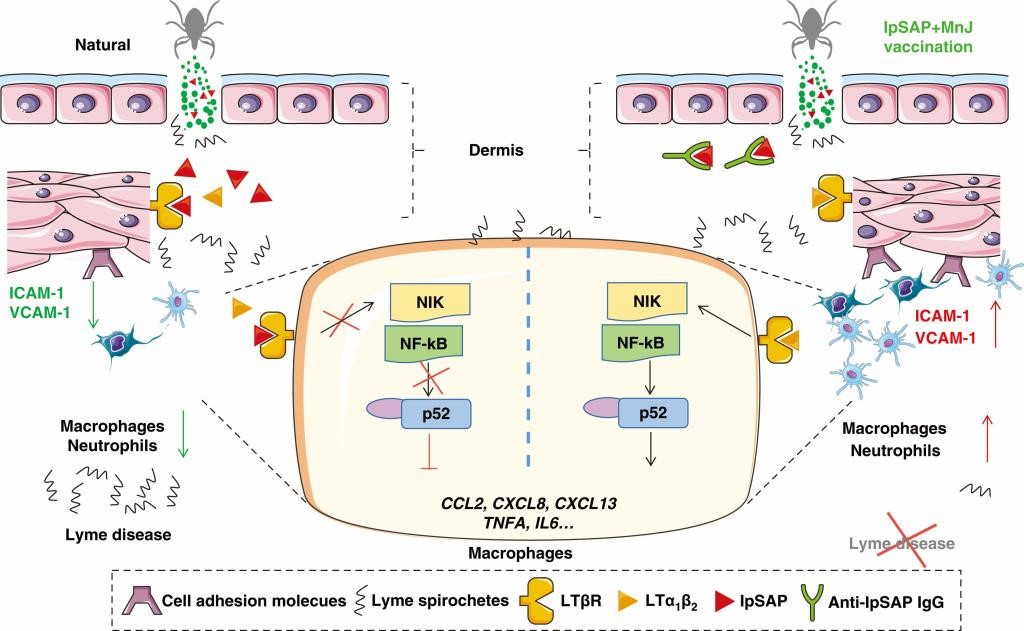
Schematic Diagram of Thesis Research
Lyme disease is the most important insect borne infectious disease in the northern hemisphere. There are nearly 480,000 Lyme cases in the United States and nearly 230,000 Lyme cases in Western Europe every year. Lyme disease is mainly transmitted by ticks, and its pathogen is Borrelia burgdorferi. The transmission of tick infection has brought a huge economic burden to the global livestock industry. For example, it is estimated that the external parasitic ticks, Rhipicephalus microplus, cause losses of 2.5 billion US dollars every year in the whole tropical and subtropical regions. With the rapid change of contemporary urbanization, deforestation, climate change and the interaction between human and animal habitats, the threat of tick borne diseases (TBDs) to human and animal health has increased significantly. In this study, the 15 kDa protein IpSAP was found in the saliva of Ixodes persulcatus, targeting the LT-βr receptor. IpSAP promotes the spread of B. garinii by inhibiting LT-βr receptor and downstream signal transduction, and forming early local immunosuppression at the site of Borrelia infection in mice. Further studies showed that mice immunized with IpSAP recombinant protein and MnJ adjuvant could effectively resist the transmission of Lyme disease spirochete mediated by ixodes. This result not only deepens the understanding of the molecular mechanism of tick-borne Lyme disease and clarifications of key vector and host molecules during transmission, but also provides new ideas for the development of novel vector-targeted Lyme disease vaccines.
Professor Jin Lin is a high-level talent introduced to SXAU in 2021. This year, he was selected as one of the first batch of cultivation objects of "Excellent Youth Cultivation Project of Shanxi Agricultural University". This research was supported by SXAU's "Outstanding Youth Cultivation Project" and other projects. Professor Jin Lin is the first author of the paper, and Jiang Baogui, an associate researcher of Beijing Institute of Microbiology and Epidemiology, is the co-first author. Lai Ren, a researcher of Kunming Institute of Zoology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, is the main corresponding author, and Cao Wuchun, a researcher of Beijing Institute of Microbiology and Epidemiology, and Professor Shahid Karim of University of South Mississippi are the co- corresponding authors.